Topic: Minimally Invasive Surgery for HCC
A Special Issue of Hepatoma Research
ISSN 2454-2520 (Online) 2394-5079 (Print)
Submission deadline: 15 Aug 2020
Guest Editor(s)
Ho-Seong Han, MD, PhD
Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Republic of Korea.
President-elect of Korean Society of HBP Surgery, President of the Korean Study Group of Laparoscopic Liver Surgery, ex-Chairman of Korean Society of Endoscopic & Laparoscopic Surgery, Chairman of the Korean Society of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (KSPEN), Vice President of IASMEN(International Association of Surgical Metabolism and Nutrition), treasurer of IASGO.
President-elect of Korean Society of HBP Surgery, President of the Korean Study Group of Laparoscopic Liver Surgery, ex-Chairman of Korean Society of Endoscopic & Laparoscopic Surgery, Chairman of the Korean Society of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (KSPEN), Vice President of IASMEN(International Association of Surgical Metabolism and Nutrition), treasurer of IASGO.
Special Issue Introduction

Special Issue webinar: Minimally Invasive Surgery for HCC
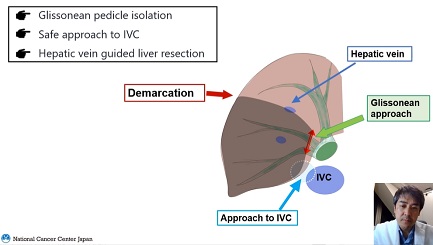
With many reports on encouraging outcomes for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), laparoscopic liver resection has been accepted as an attractive alternative to open liver resection for treatment for HCC. However, still laparoscopic liver resection is still considered as difficult procedure, especially for major resection. In the 1st and 2nd consensus meeting on laparoscopic liver resection meeting, it was stated that major resection still has a risk associated with its novelty. And there are several limits in technical aspects. When the tumor is located at postero-superior area, it is still difficult to perform laparoscopic liver resection. Cirrhosis is still a limiting condition for this surgery. There is also the limit in control bleeding when it occurs. However, with the accumulation of the experiences on laparoscopic liver resection, this procedure is more easily performed than before. Anatomic liver resection has been reported to have oncological benefit. And there are reports that remnant liver ischemia after liver resection has an adverse effect on survival. This procedure should be performed very precisely and meticulously. Recently, there is a new trend to perform robotic-assisted liver resection. Robotic-assisted liver resection has advantages of ergonomic conveniences and short learning curve. However, there is still a shortage of adequate equipment such as CUSA.
With the evident advantage associated with minimal invasive surgery, minimally invasive liver surgery will be performed more frequently in the future.
Submission Deadline
15 Aug 2020
Submission Information
For Author Instructions, please refer to https://www.oaepublish.com/hr/author_instructions
For Online Submission, please login at https://oaemesas.com/login?JournalId=hr&SpecialIssueId=403
Submission Deadline: 15 Aug 2020
Contacts: Victoria Lee, Assistant Editor, editor_Victoria@hrjournal.net