Topic: Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Therapeutic Resistance
A Special Issue of Hepatoma Research
ISSN 2454-2520 (Online) 2394-5079 (Print)
Submission deadline: 15 May 2024
Guest Editor(s)
Special Issue Introduction
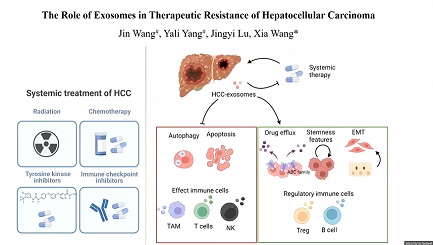
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common human malignancies with poor prognosis, and it is ranked the fourth cause of cancer mortality worldwide. Although surgical resection and liver transplantation have already been used for early-stage HCC treatment, most of the patients were diagnosed at late stages and lost the chance for curative therapy. Currently, several multi-kinase inhibitors, including sorafenib, regorafenib, and lenvatinib have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as first-line or second-line treatment for unresectable advanced HCC. However, the benefit to patients from the therapy is very limited due to the high rate of drug resistance and tumor relapse. The emergence of immune checkpoint inhibitors such as monoclonal antibody directed against the programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) has shown promising results in HCC recently. Nevertheless, only a small fraction of patients responds to immune-based therapies. Thus, further investigation of the molecular mechanisms in therapeutic resistance and the development of novel therapeutic drugs is urgently needed.
Submission Deadline
15 May 2024
Submission Information
For Author Instructions, please refer to https://www.oaepublish.com/hr/author_instructions
For Online Submission, please login at https://oaemesas.com/login?JournalId=hr&SpecialIssueId=hr220428
Submission Deadline: 15 May 2024
Contacts: Ada Zhong, Assistant Editor, editor_ada@hrjournal.net